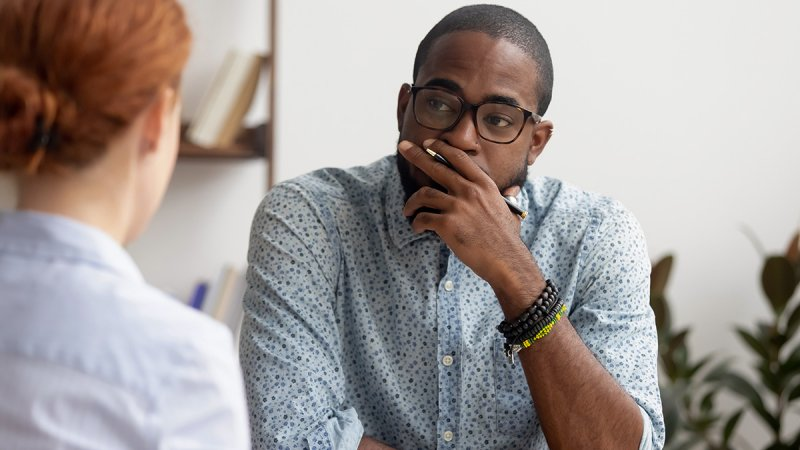
Property is a resource of financial value and something that an organisation needs in order to do its work. Intellectual property can set organisations apart from competitors and help maintain longevity and profitability, and this is exactly why it needs protecting just as much as the physical assets.
Employees are the brainpower behind intellectual property because they are the ones that come up with all the ideas such as brands, inventions, trade secrets and software.
Understanding Intellectual Property
To keep it simple, intellectual property includes the ideas and designs that a company has. Whilst physical property is the tangible aspect to the company, intellectual property is the intangible side to the company that makes them different to others.
Intellectual property is a bit more confusing than physical property when it comes to categorising it. If you have an idea for a book, that isn’t intellectual property, however, if you were to write it down, it becomes intellectual property that needs protecting.
Intellectual property can:
- Have more than one owner
- Belong to people or businesses
- Be sold or transferred

-
Protecting Intellectual Property
Lending a USB stick to somebody, with intellectual property contained within, poses many risks. The stick could get lost and intellectual property could be opened and saved on outsider devices. Intellectual property is confidential information and should be treated as such.
Whilst protecting physical property can be a case of keeping it under lock and key, protecting intellectual property can be much more difficult because they are intangible. As a result, it ends up being a case of using documents and agreements as protection. By protecting your intellectual property, it means that you can take legal action against anyone that tries to steal or copy it.
It’s important when circulating confidential information that it stays on a need-to-know basis. All parties involved in knowing this information need to sign a non-disclosure agreement. This is a legal contract that protects any non-public business information whereby the people in the know agree not to disclose it for a defined period of time.
A patent gives exclusive rights to an inventor over their new invention for a limited time period. During this time, nobody else can make, use or copy the invention.
A registered design protects the style of a product, whether that is its shape, product packaging or surface design. Patent and registered designs are similar, a patent covers a new invention whilst a registered design focuses on the look of a product.
A trademark is a logo, words, or a combination of both, that represents a brand or an organisation. It helps to keep a brand unique and identifiable.
Copyright gives creators of original work, certain exclusive rights. This law gives the owner of a work the right to say how other people can use it.
When creating a business plan, it’s important to consider which assets need to be protected and how.