Under GDPR, a data subject has the right to obtain confirmation as to whether or not their personal data is being processed. The right to receive data under a subject access request must not adversely affect the rights and freedoms of others. You cannot comply with a subject access request if it would adversely affect someone else’s rights. If the information is subject to legal privilege or concerns a third party, it may not be able to be released.
What is a subject access request?
Data subjects are entitled to find out what personal data is held about them by an organisation, why the organisation is holding it and who else knows the information. The process of finding this out is known as a subject access request, or SAR.
A subject access request is not the same as a Freedom of Information (FOI) request. An FOI request covers all information held only by public authorities, but not personal information about the person making the request. If you are not a public body or otherwise covered by FOI legislation, an FOI request cannot be made to you.
How should you respond to a subject access request?
GDPR mandates certain procedures when dealing with subject access requests.
Provide the information for free
Data must be provided for free. A reasonable fee, based on the administrative cost for providing the data, can only be charged when a request is manifestly unfounded, excessive or repetitive, or if further copies of the same data are requested.
One month to respond
The information must be provided without delay and within at least one month of receiving the request. If requests are complex or numerous, the deadline can be extended to three months, but the subject must be informed of the extension and its justification within the one-month deadline.
Provide a response
Data subjects must have the option of making the request electronically (such as by email or online form), and the information provided in those means too. The information must be provided in a commonly used file format, or where possible, through remote access to a secure system that gives direct access to the data.
Failure to respond
Failure to respond to a subject access request within the time period permitted may result in the individual bringing an action for damages or reporting the matter to the appropriate regulatory body, such as the Information Commissioner’s Office in the UK, which may well give rise to an investigation by that body.
Data portability right under GDPR
Individuals also have the right to have their personal data transferred to them in a structured, commonly used and machine-readable (i.e. electronic) form so that it may be transferred to another data controller without hindrance. The controller can be required to transmit the data directly to another controller where it is technically feasible to do so.
Whereas subject access is a broad right, the portability right is narrower. It applies:
- To personal data which is processed by automated means (i.e. no paper records)
- To personal data which the data subject has provided to the controller
- Only where the basis for processing is consent, or where the data is being processed to fulfil a contract or take steps in preparation for a contract
Exemptions
There are various exemptions where the organisation may not have to respond to the subject access request. Generally, information that may adversely affect others’ rights, such as intellectual property rights or trade secrets, can be withheld.
Other examples of exemptions include:
- Information on a subject’s mental or physical health provided to a court in proceedings concerned with the care of children
- Information provided to regulatory bodies
- Deliberations undertaken by judges or connected with legal proceedings
- Legally privileged information
- Data processed only for research, historical or statistical purposes
- Information held by journalists seeking to expose wrongdoing
- Information held for fulfilling an employment law obligation
- Information that relates to a money laundering or terrorist financing investigations
- Information relating to national security
However, you cannot refuse to provide all information on the grounds that some of the information may be exempt.
Other limiting provisions
If you hold large amounts of data on someone, you may ask them to specify what they are looking for in more detail.
The purpose of making a subject access request is to confirm the accuracy of data held and the lawfulness of processing to enable the subject to exercise their right to correct inaccurate data or object to it being processed. Subject access requests made for other, non data protection related purposes could be rejected.
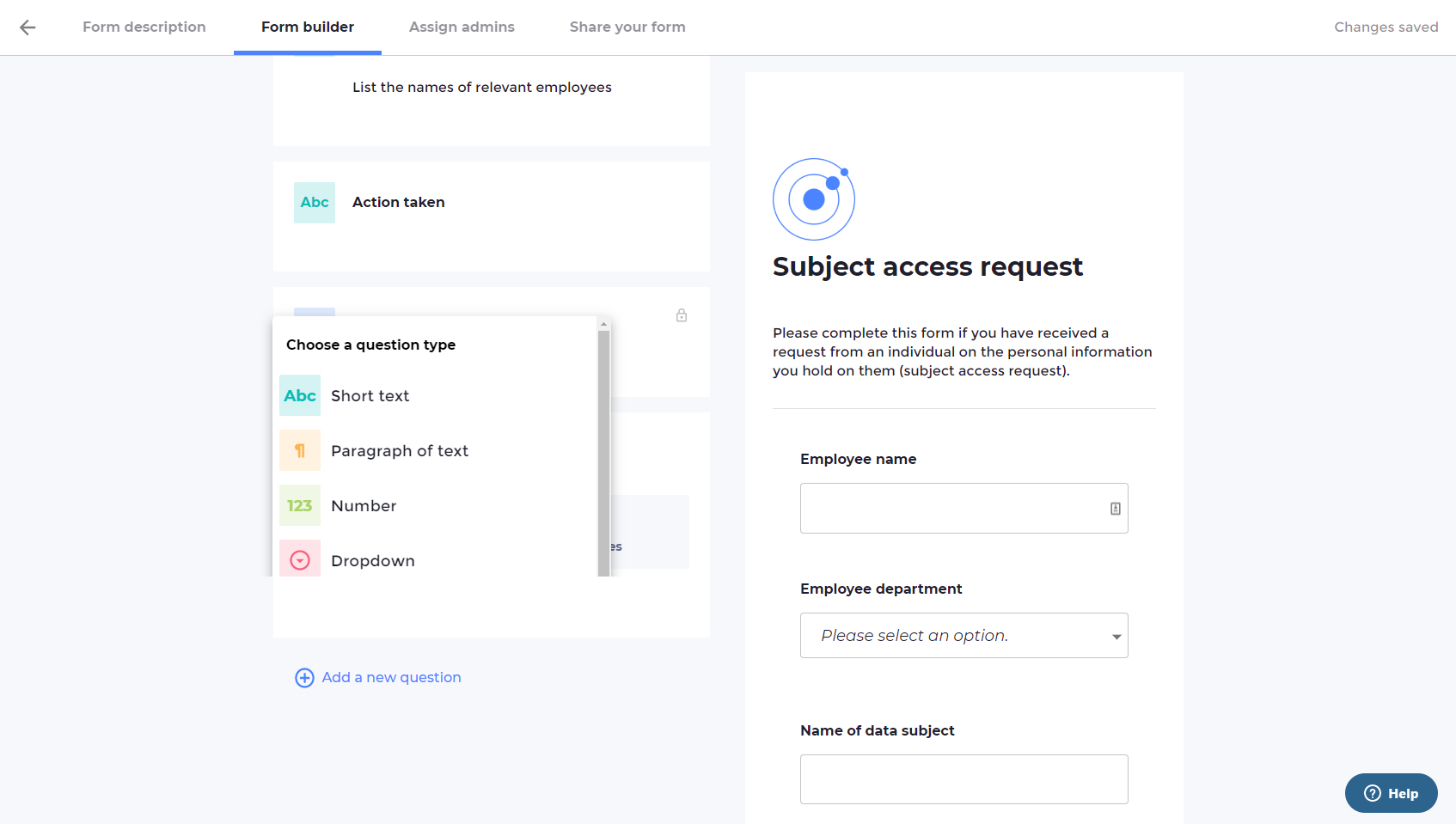
VinciWorks’ subject access request portal

VinciWorks’ subject access request portal allows employees to report all subject access requests received. Administrators receive notifications as soon as the form is completed and can easily track progress on any further action that is required. We have also created a bank of template forms that can easily be customised to suit any organisation and industry.